Configuring Script Settings in CatchPulse Policy
Scripts are widely used to automate various tasks in a network, such as backing up data, updating system configurations, and managing network resources. However, if these scripts are not properly managed, they can become a potential source of vulnerability, allowing attackers to execute malicious code on your devices. To reduce the risk of such attacks, ensuring that both the interpreter and the script file are trustworthy is important.
To execute a script, you must trust the interpreter and the script file. The script interpreter is responsible for executing the script and will not open any file it does not trust.
Jump to:
Disabling using Default Script
Adding New User-Defined Script
Disabling using Default Script
To disable using Default Script
-
From the main navigation bar, go to CatchPulse → Policy.
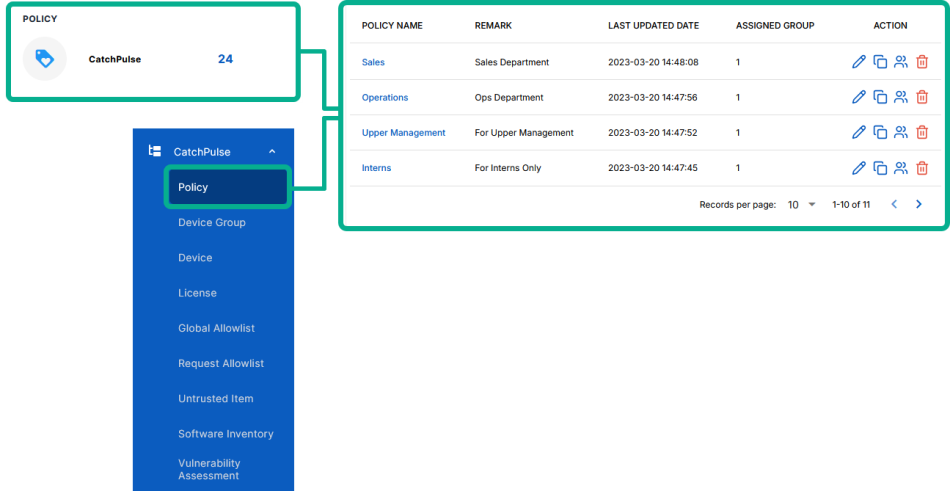
-
Do one of the following:
-
To disable using Default Script in a new policy, click on the Add Policy button located at the top right corner of the Policy page, or
-
To disable using Default Script in an existing policy, select a policy and click on the corresponding
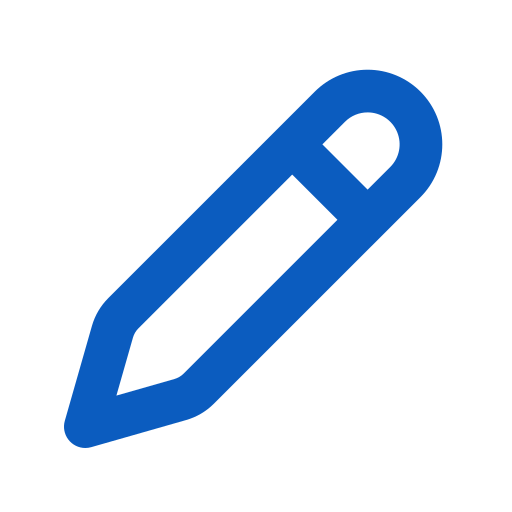 button.
button.
-
-
On the Policy page, under Manage → Script.
-
Turn off Use Default Script switch.
Adding New User-Defined Script
To add New User Script
-
From the main navigation bar, go to CatchPulse → Policy.

-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a New User-Defined Script to a new policy, click on the Add Policy button located at the top right corner of the Policy page, or
-
To add a New User-Defined Script to an existing policy, select a policy and click on the corresponding
 button.
button.
-
-
On the Policy page, under Manage → Script.
-
Click Add New User-Defined from the top right corner of the Script page.
-
On the Add Script display box, enter the interpreter; the executable that runs the script and its associated file extension.
-
(Optional) Select Add another to continue adding more Scripts.
-
Click Add to add Script.
The notification panel at the bottom of the page indicates the Script was added successfully.
Deleting User-Defined Script
To delete User-Defined Script
-
From the main navigation bar, go to CatchPulse → Policy.

-
Select a policy and click on the corresponding
 button.
button. -
On the Policy page, under Manage → Script.
-
Under the User-Defined Script tab, select a Script and click on the corresponding
 button.
button. -
When prompted to remove Script, select Delete.
The notification panel at the bottom of the page indicates the Script was deleted.
More information
Support and feedback
Should you encounter any issues using the SecureAge Central with any of the mentioned or missed requirements above, you can always write to us a docs@secureage.com.
This page was last updated: September 09, 2025
